When it comes to ensuring the smooth operation of machinery and equipment, the choice of grease line tubing and fittings plays a crucial role. These components are integral to the lubrication system, facilitating the efficient transfer of grease to critical areas that require regular maintenance. Selecting the right grease line tubing and fittings not only enhances performance but also extends the lifespan of the machinery, reducing the likelihood of breakdowns and costly repairs.
In this article, we will delve into essential tips that will guide you in choosing the optimal grease line tubing and fittings for your specific applications. From understanding material compatibility and pressure ratings to considering the installation environment, each factor plays a significant role in the overall effectiveness of your grease delivery system. By carefully evaluating these elements, you can ensure that your lubrication systems are both reliable and efficient, ultimately promoting better performance and productivity in your operations. Whether you are maintaining heavy machinery or automotive applications, making informed choices regarding grease line tubing and fittings is vital for achieving optimal results.
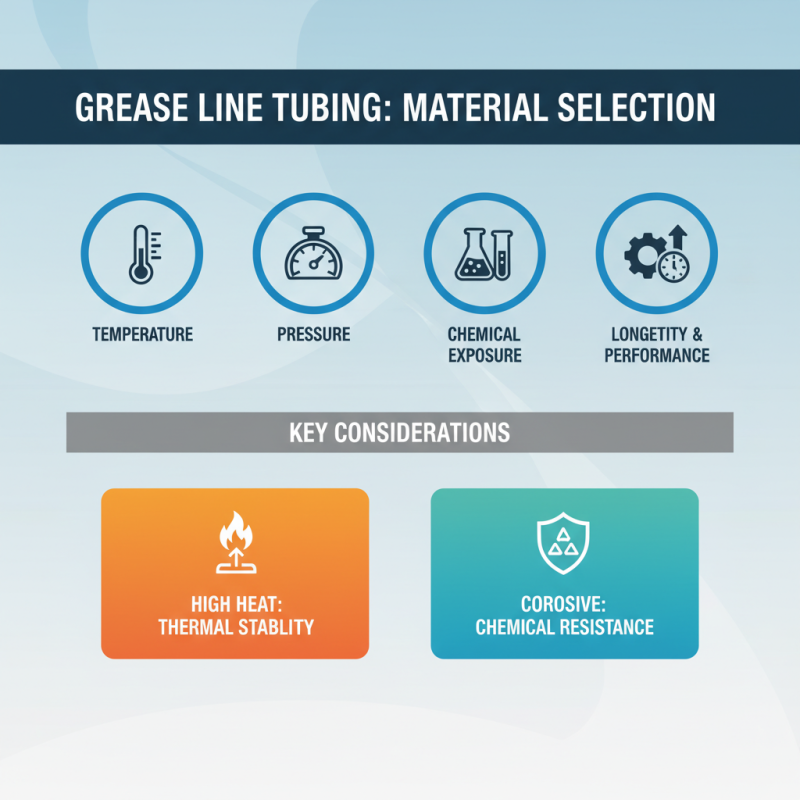
When selecting grease line tubing materials, several key considerations can significantly influence the performance and longevity of your lubrication system. First and foremost, it’s essential to choose materials that can withstand the operating conditions of your environment. Factors such as temperature, pressure, and exposure to chemicals should guide your material selection. For instance, high-temperature applications may require materials with excellent thermal stability, while corrosive environments will need tubing that can resist chemical degradation.
Tip: Always assess the compatibility of the tubing material with the type of grease used. This ensures that the grease won't degrade the tubing, which could lead to system failures and increased maintenance costs.
Additionally, the flexibility and diameter of the tubing can impact the flow rate and ease of installation. Choosing the right diameter is crucial for ensuring optimal grease delivery to the designated points, while flexibility can help in navigating around obstacles during installation.
Tip: Before making a final decision, it's advisable to evaluate the installation space and any potential bends or connections in the layout, as this can affect the choice of fittings as well. Properly matched fittings facilitate a leak-free environment, which is essential for maintaining system integrity.
When it comes to grease line fittings, it’s crucial to understand the variety of options available to ensure optimal performance in lubrication systems. The primary types of grease fittings, often referred to as grease nipples, include standard, angled, and extended fittings. Standard fittings are the most common and are typically used in applications where a straight line connection is feasible. They ensure easy access for grease guns and provide reliable sealing to prevent leakage.
Angled fittings, on the other hand, are designed to allow connection at awkward or tight angles, making them ideal for spaces that are difficult to reach. Their unique design helps accommodate various installation scenarios, enhancing flexibility in maintenance tasks. Extended fittings are particularly useful in areas requiring longer reach, enabling operators to easily access and lubricate components without interference from surrounding machinery. Understanding these types of grease line fittings and their specific applications is essential for maintaining equipment efficiency and prolonging service life.
When selecting grease line tubing and fittings, several factors significantly influence the overall performance of the grease line systems. One primary element is the material composition of the tubing. Steel and high-density polyethylene (HDPE) are popular choices, but each material has specific temperature and pressure tolerances that can impact functionality. For instance, if a system operates under high pressure, selecting a tubing material that can withstand such conditions without compromising integrity is crucial. Additionally, assessing the chemical compatibility of the tubing with various grease types ensures longevity and reliable operation.
Another critical aspect is the size and diameter of the tubing and fittings. Proper sizing not only facilitates adequate grease flow but also reduces the risk of clogs or blockages that could lead to system failures. Oversized tubing may result in sluggish performance, whereas undersized tubing can cause excessive pressure buildup. Furthermore, the layout of the grease line system, including bends and turns, should be considered, as these can create turbulence and affect overall performance. Ensuring smooth transitions and minimizing sharp angles will help maintain efficient grease distribution throughout the system.
Maintaining grease line tubing and fittings is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of lubrication systems. Regular inspection is key; operators should conduct routine checks for signs of wear and tear, leaks, or blockages. It’s important to clean the tubing and fittings regularly to prevent the buildup of grease that can hinder flow and lead to premature failure. Using approved cleaning agents and following manufacturer guidelines ensures that components remain free from contaminants that could impair their function.
In addition to routine maintenance, proper installation practices are vital. Ensuring that tubing and fittings are correctly aligned and securely fastened minimizes stress on the joints, which can lead to leaks. Furthermore, monitoring operating temperatures and pressures can provide early indicators of potential issues. Operators should also keep a close eye on the lubrication schedule, as infrequent greasing can result in insufficient lubrication and increased wear. Implementing these maintenance practices not only extends the life of grease line systems but also enhances overall operational efficiency.
| Dimension | Description | Material | Working Pressure (psi) | Temperature Range (°F) | Maintenance Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/4 inch | Standard grease line for small machinery | Polyurethane | 3,000 | -40 to 200 | Every 6 months |
| 3/8 inch | Optimal for mid-sized equipment | Nylon | 4,000 | -20 to 180 | Every 3 months |
| 1/2 inch | Heavy-duty grease line for industrial use | Stainless Steel | 5,000 | -30 to 250 | Monthly |
| 3/4 inch | For large industrial machines | Rubber | 6,000 | -10 to 220 | Every 2 months |
When installing a grease line system, avoiding common mistakes is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity. One frequent error is the miscalculation of tubing length. According to industry reports, nearly 30% of grease line failures stem from improper tubing lengths, leading to excessive pressure drops and inefficiencies. Proper measurement and accounting for bends and turns in the piping can significantly enhance the system's effectiveness. It's vital to use precise measuring techniques to avoid overextending or underestimating the needed tubing.
Another critical aspect to consider is the selection of fittings. Choosing incompatible fittings can lead to leaks or system failures. Data from lubrication industry studies shows that approximately 25% of maintenance issues arise from poor fitting compatibility. Professionals should ensure that selected fittings match both the tubing material and the grease type, adhering to the manufacturer specifications to prevent issues down the line. In addition, regular inspections and maintenance schedules can help identify early signs of wear or incompatibility, further extending the system's operational life and reliability.





